Description
Description
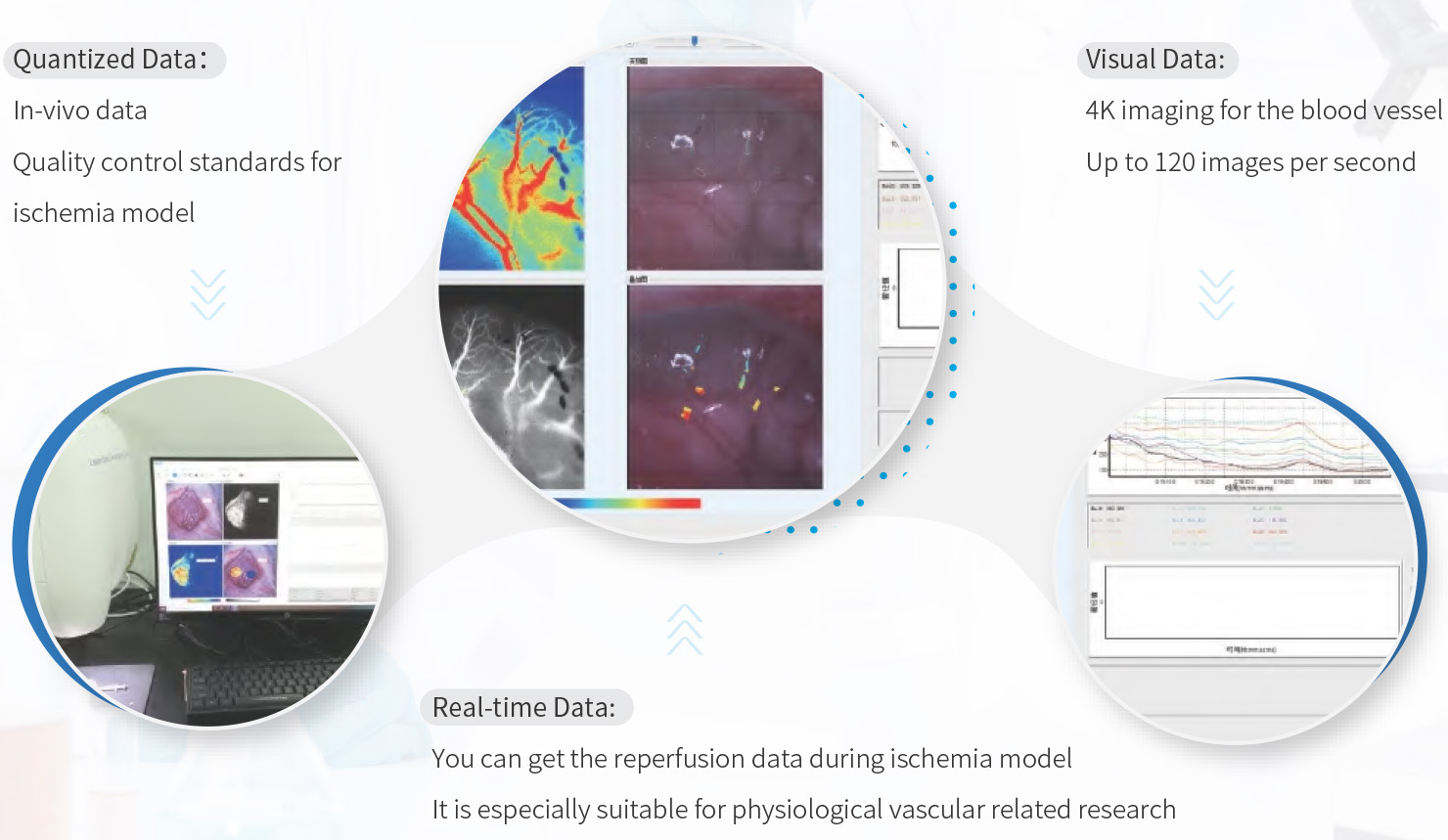
VIVO-LSI is based on the LSCI (Laser Speckle Contrast Analysis Imaging ) technology design, non-invasive with non-contact, high time resolution, high spatial resolution, and full-field rapid imaging. It provides real-time dynamic blood flow monitoring and recording for research, perfusion evaluation, such as MCAO, cerebral blood flow. compared with lase doppler imaging, it can realize full field video imaging function.
Applications:
- Cerebral blood flow, MCAO model
- Cortical Spreading Depression (CSD)
- Hind/Critica Limb Ischaemia (HLI)/(CLI)
- Neuro-Vascular Coupling
- Burn Assessment, Traumatic Brain Injury(TBI) and Sepsis
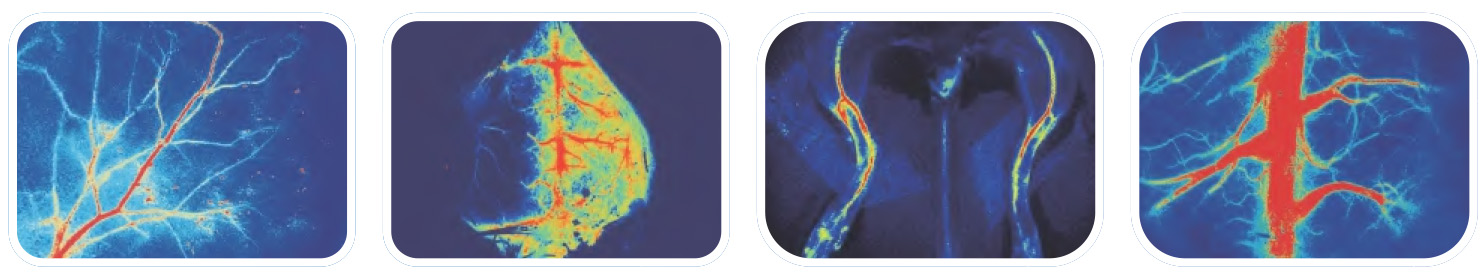
Features
The VIVO-LSI can be used to measure the microcirculation of any exposed superficial vessels, such as the cortex, mesentery, lower limbs, and spinal cord. It is a popular choice and has been used in more than 100 colleges, universities, and research institutes throughout the world. It offers:
- Non-invasive, real-time, full-field imaging with high-definition; no need for scanning, no need of contact, no need of contrast for imaging
- 12x Optical lens, autofocus, electrical zoom, allows researchers to adjust the image area as they need
- Built-in Basler camera delivering high definition and high speed imaging. Image resolution up to 2048 x 2048 pixels and high frame rate speed of up to 120 frames per second
- Dual 3.0 USB interface for fast data transmission, high frame rate and high resolution
- A Thorlabs laser is used to output laser with good coherence to ensure the stability of baseline data and obtain the fluctuation data of real blood perfusion
- Blood flowmeter (the volume of blood perfusion expressed as conventional unit PU) to observe the relative changes in the velocity of blood flow by combining image data with perfusion data
- The global PU value is adopted to quantify the values of blood perfusion and obtain the objective data changes in the velocity of blood flow.
- Combining the image data and perfusion data, the velocity of blood flow can be observed by the pictures, and the relative velocity of blood flow can be judged by different colors. (Perfusion Unit)
- Hardware structures including instruction laser and Cardan gimbals and humanized software operation mode make the whole system easy to use
What is Speckle Contrast Analysis?
Speckle flow techniques are based on the changes over time of the dynamic speckle pattern generated by motion in the sample. In these techniques, this changing speckle pattern is recorded with a camera that has an integration time in the order of the speckle decorrelation time (i.e., in the millisecond range). Due to the long integration time compared to the typical decorrelation time of the speckle pattern, the speckle pattern will be blurred in the recorded image. The level of blurring is quantified by the speckle contrast.
Why choose the VIVO-LSI
Specifications
| Model | VIVO-LSI |
| Scale | 0 – 5000PU |
| Imaging acquisition rate | Up to 120 FPS |
| Working distance | 10 – 35 cm |
| Image size | 1.57 × 1.57mm – 90 × 90mm |
| Image camera pixels | 4.2 million(2048 × 2048) |
| Max resolution | Up to 3μm/pixel |
| Zoom range | 12× optical zoom lens with auto-focus |
| Wavelength | 785nm |
Case Study
Use the laser speckle to observe changes in cerebral blood flow after lymphatic ablation and quantitative analysis
- Use the laser speckle to observe changes in cerebral blood flow after lymphatic ablation, and quantitative analysis. Explore whether meningeal lymphatics are involved in clearing extravasated erythrocytes in CSF after SAH.
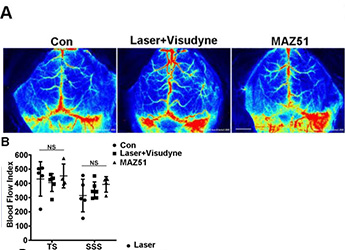
Real-time monitor the regional velocity and distribution of blood flow and perfused vessel for sciatic nerve and foot pads
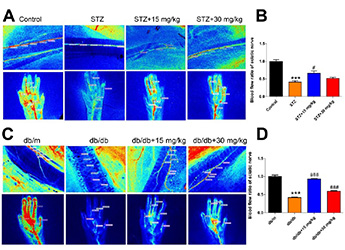
- Use LSCI to real-time detect regional velocity and distribution of blood flow and perfused blood vessel of sciatic nerve and foot pads, and also analyze image to better evaluate the therapeutic effect of small molecule substances on diabetes.
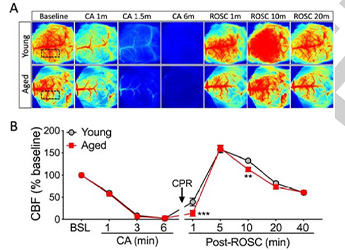
Detect the changes of the cerebral cortex blood perfusion of a Cardiac arrest (CA) and Return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) mouse model
- The main purpose of the UPR is to restore ER homeostasis, and promote cell survival. It has been well established that brain I/R insult caused by transient ischemic stroke or CA/resuscitation leads to ER stress and subsequent activation of the UPR. The previous study has demonstrated that the XBP1s/HBP/O-GlcNAc axis functions in the brain, and is activated after ischemic stroke or CA (6, 8). Here, the goal was to clarify the effect of this axis on functional outcome after CA in young and aged mice.